
As concerns about climate change intensify, homeowners are increasingly seeking sustainable solutions for their homes. Sustainable home heating and cooling systems are not only environmentally friendly but also offer significant financial benefits. These systems harness renewable energy sources and utilize energy-efficient technologies to reduce carbon footprints and lower energy bills.
This guide delves into the diverse range of sustainable heating and cooling systems available, exploring their advantages, disadvantages, and suitability for various home types and climates. We’ll discuss everything from geothermal heat pumps to solar thermal heating and passive cooling techniques, providing practical tips for homeowners looking to make their homes more energy-efficient and environmentally responsible.
Types of Sustainable Heating Systems
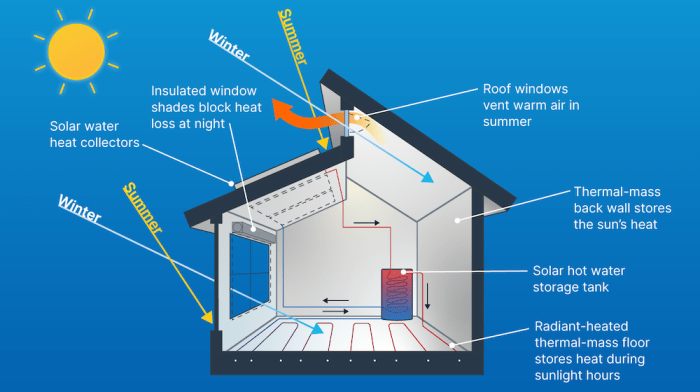
Sustainable heating systems are crucial for reducing our reliance on fossil fuels and minimizing our environmental impact. These systems harness renewable energy sources and improve energy efficiency, offering a greener and more cost-effective approach to heating our homes.
Geothermal Heat Pumps
Geothermal heat pumps utilize the stable temperature of the earth to heat and cool homes. They work by transferring heat from the ground to your home in the winter and from your home to the ground in the summer. These systems are highly efficient and can reduce energy consumption by up to 70% compared to traditional heating systems.
- Efficiency: Geothermal heat pumps have a high Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER) of 3.0 to 6.0, meaning they use less energy to produce the same amount of heat.
- Cost-effectiveness: Although the initial installation cost is higher than traditional systems, the long-term savings on energy bills make them cost-effective over time.
- Environmental Impact: Geothermal heat pumps have a minimal environmental impact, as they use renewable energy and emit very little greenhouse gases.
Solar Thermal Heating
Solar thermal heating systems use the sun’s energy to heat water for domestic use, including showers, baths, and space heating. They consist of solar panels that absorb solar radiation and transfer heat to a fluid, which then heats the water.
- Efficiency: The efficiency of solar thermal systems depends on factors such as panel size, location, and weather conditions. They can achieve efficiency rates of 50% to 70%.
- Cost-effectiveness: The initial installation cost is relatively high, but the long-term savings on energy bills make them cost-effective.
- Environmental Impact: Solar thermal systems have a minimal environmental impact as they use renewable energy and emit no greenhouse gases.
Wood-Burning Stoves
Wood-burning stoves offer a traditional and efficient way to heat homes. They burn wood to generate heat, which is then distributed throughout the home. However, it’s essential to consider the efficiency and environmental impact of wood-burning stoves.
- Efficiency: Modern wood-burning stoves have high efficiency rates of 70% to 80%, meaning they convert a larger portion of the wood’s energy into heat. However, older stoves may have lower efficiency rates.
- Cost-effectiveness: Wood-burning stoves can be cost-effective if you have access to affordable wood sources. However, the cost of wood can fluctuate and may increase over time.
- Environmental Impact: While wood is a renewable resource, burning wood releases particulate matter and other pollutants into the air. The environmental impact depends on the type of wood used, the efficiency of the stove, and the overall emissions from the burning process.
Heat Recovery Ventilation Systems
Heat recovery ventilation (HRV) systems improve indoor air quality and reduce energy consumption by recovering heat from exhaust air and transferring it to incoming fresh air. They ensure a constant supply of fresh air while minimizing heat loss.
- Efficiency: HRV systems can achieve energy savings of up to 30% by reducing the amount of energy needed to heat or cool incoming air.
- Cost-effectiveness: The initial installation cost is relatively high, but the long-term savings on energy bills and improved air quality make them cost-effective.
- Environmental Impact: HRV systems have a minimal environmental impact as they reduce energy consumption and improve indoor air quality.
| System Type | Efficiency | Cost | Environmental Impact | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Geothermal Heat Pumps | High (SEER 3.0 to 6.0) | High initial cost, but lower long-term costs | Minimal | Highly efficient, renewable energy source, reduces carbon footprint | Higher initial installation cost, requires specialized installation |
| Solar Thermal Heating | Moderate (50% to 70%) | High initial cost, but lower long-term costs | Minimal | Renewable energy source, reduces reliance on fossil fuels, can be used for both heating and hot water | Requires sufficient sunlight exposure, may not be suitable for all climates |
| Wood-Burning Stoves | Moderate (70% to 80% for modern stoves) | Lower initial cost, but wood costs can fluctuate | Moderate (depends on wood type and stove efficiency) | Cost-effective if wood is readily available, can provide a cozy atmosphere | Releases pollutants into the air, requires regular maintenance, fire hazard |
| Heat Recovery Ventilation Systems | Moderate (energy savings of up to 30%) | High initial cost, but lower long-term costs | Minimal | Improves indoor air quality, reduces energy consumption, can be used for both heating and cooling | Higher initial installation cost, requires regular maintenance |
Types of Sustainable Cooling Systems
Sustainable cooling systems play a crucial role in reducing our reliance on fossil fuels and mitigating the impact of climate change. These systems utilize various approaches to provide comfortable indoor temperatures while minimizing environmental impact.
Passive Cooling Techniques
Passive cooling techniques harness natural forces to cool buildings without relying on mechanical systems. These methods are highly energy-efficient and environmentally friendly.
- Shading: Strategic use of trees, awnings, or overhangs can block direct sunlight during peak hours, reducing solar heat gain and lowering indoor temperatures. A well-designed shade structure can reduce heat gain by up to 75%. For example, a deciduous tree can provide shade in the summer and allow sunlight in during the winter.
- Ventilation: Cross-ventilation, using strategically placed windows and doors, allows cool air to circulate through a building, replacing warm air. This technique is particularly effective in areas with prevailing winds. A well-designed ventilation system can reduce indoor temperatures by 5-10 degrees Fahrenheit. For instance, a simple window fan can create a cross-breeze, drawing in cooler air from outside.
- Evaporative Cooling: This technique uses the natural process of evaporation to cool air. Water is evaporated, absorbing heat from the surrounding air, which is then circulated through the building. This method is effective in dry climates where humidity is low. A typical evaporative cooler can reduce indoor temperatures by 15-20 degrees Fahrenheit. An example is using a swamp cooler, which draws air over a wet pad, evaporating the water and cooling the air.
Geothermal Cooling Systems
Geothermal cooling systems utilize the stable temperature of the earth to cool buildings. These systems use a closed-loop system to circulate water or antifreeze through underground pipes, absorbing heat from the ground. The cooled water is then used to chill air in the building.
- Advantages:
- Highly energy-efficient, reducing energy consumption by up to 70% compared to traditional air conditioners.
- Environmentally friendly, as they don’t use refrigerants that contribute to ozone depletion.
- Long lifespan, typically lasting for 20-25 years.
- Reduced operating costs due to lower energy consumption.
- Disadvantages:
- High initial installation costs, as they require extensive underground piping.
- Not suitable for all climates, as they rely on consistent ground temperatures.
- May require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance.
Solar-Powered Air Conditioners
Solar-powered air conditioners use solar energy to power the cooling system. This technology is becoming increasingly efficient and cost-effective.
- Advantages:
- Environmentally friendly, as they rely on renewable energy source.
- Reduced energy bills, as they eliminate reliance on the electrical grid.
- Suitable for remote locations with limited access to electricity.
- Disadvantages:
- High initial installation costs, as they require solar panels and inverters.
- Performance can be affected by weather conditions, such as cloud cover.
- May require battery storage to provide cooling during periods of low solar irradiance.
Comparison of Sustainable Cooling Methods
| Cooling Method | Effectiveness | Cost | Environmental Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Passive Cooling | Moderate, effective in specific climates | Low | Very low |
| Geothermal Cooling | High, efficient and reliable | High (initial installation) | Very low |
| Solar-Powered Air Conditioning | Moderate, performance depends on solar irradiance | High (initial installation) | Low |
Government Incentives and Rebates
Many governments offer incentives and rebates to homeowners who install sustainable heating and cooling systems. These programs aim to promote energy efficiency, reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and encourage the adoption of renewable energy sources.
Eligibility Criteria and Application Processes
To be eligible for these programs, homeowners must typically meet specific criteria, such as:
- Residing in a designated area or region.
- Meeting income requirements.
- Installing a qualified sustainable heating or cooling system.
- Completing the application process and providing necessary documentation.
The application process usually involves submitting an application form, providing proof of residency and income, and obtaining a contractor’s certification for the installed system.
Examples of Successful Implementations
Several successful implementations of sustainable home heating and cooling systems with government support have been observed across different regions.
- In the United States, the Residential Clean Energy Credit offers tax credits for homeowners who install solar panels, geothermal heat pumps, and other eligible renewable energy systems. This program has helped to significantly increase the adoption of renewable energy technologies, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and promoting energy independence.
- The Canadian government’s EcoEnergy Retrofit Program provides grants and rebates for homeowners who undertake energy-efficient renovations, including the installation of high-efficiency heating and cooling systems. This program has been instrumental in reducing energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions in Canadian households.
- The European Union’s Green Deal includes initiatives to support the transition to a more sustainable building sector. These initiatives provide financial assistance for the installation of sustainable heating and cooling systems, energy-efficient insulation, and other energy-saving measures.
Energy Efficiency Tips for Sustainable Homes

Making your home more energy-efficient can significantly reduce your environmental impact and save you money on utility bills. By implementing energy-saving strategies, you can create a more comfortable and sustainable living environment.
Proper Insulation and Sealing
Insulation acts as a barrier, preventing heat from escaping in the winter and keeping it out in the summer. Sealing air leaks can significantly reduce energy loss and improve the overall efficiency of your home.
- Insulate your attic and crawl spaces: Properly insulating these areas can significantly reduce heat loss in the winter and heat gain in the summer.
- Insulate your walls: Wall insulation helps to maintain a comfortable indoor temperature year-round, reducing the strain on your heating and cooling systems.
- Seal air leaks: Air leaks can occur around windows, doors, electrical outlets, and plumbing fixtures. Using weatherstripping, caulk, or foam sealant can help to prevent drafts and improve energy efficiency.
Smart Thermostats and Automation
Smart thermostats offer programmable temperature settings and can learn your heating and cooling preferences, optimizing energy consumption. Automation systems can further enhance energy efficiency by controlling lighting, appliances, and other systems based on your schedule and preferences.
- Programmable thermostats: Set different temperatures for different times of day, such as lower temperatures at night when you are sleeping or when you are away from home.
- Smart thermostats: These devices learn your heating and cooling preferences and can automatically adjust temperatures based on your schedule and the weather.
- Home automation systems: These systems can control lighting, appliances, and other systems based on your schedule and preferences, further reducing energy consumption.
Using Energy-Efficient Appliances and Lighting
Choosing energy-efficient appliances and lighting can significantly reduce your home’s energy consumption. Look for Energy Star-rated appliances and LED bulbs, which offer significant energy savings compared to traditional models.
- Energy Star-rated appliances: These appliances meet strict energy efficiency standards and can save you money on your utility bills.
- LED lighting: LED bulbs use significantly less energy than traditional incandescent bulbs and last much longer.
- Replace older appliances: If your appliances are outdated, consider replacing them with newer, more energy-efficient models.
Optimizing Window Placement and Shading
Window placement and shading play a crucial role in maximizing natural light and minimizing heat gain in the summer. Strategic window placement can reduce the need for artificial lighting and cooling, while shading can prevent excessive heat from entering your home.
- Maximize natural light: Place windows on the south side of your home to maximize natural light and solar heat gain in the winter.
- Minimize heat gain: Use awnings, trees, or other shading devices to block direct sunlight from entering your home during the summer months.
- High-performance windows: Consider using double- or triple-pane windows with low-e coatings to reduce heat loss in the winter and heat gain in the summer.
The Future of Sustainable Home Heating and Cooling
The field of sustainable home heating and cooling is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements and a growing awareness of the need for energy efficiency and environmental responsibility. This dynamic landscape promises exciting innovations that will shape the future of how we heat and cool our homes.
Integration with Smart Home Technology
The integration of sustainable heating and cooling systems with smart home technology is transforming the way we manage energy consumption. Smart thermostats, for example, can learn our preferences and automatically adjust temperatures to optimize comfort and energy efficiency. They can also be programmed to adjust temperatures based on our schedules, ensuring that our homes are not heated or cooled unnecessarily.
- Remote control: Smart thermostats allow us to control our heating and cooling systems remotely, enabling us to adjust temperatures from anywhere with an internet connection. This can be especially useful for pre-heating or pre-cooling our homes before we arrive, ensuring optimal comfort upon arrival.
- Energy monitoring: Smart systems provide real-time energy consumption data, allowing us to track our energy usage and identify areas for improvement. This information can empower us to make informed decisions about our energy habits and reduce our environmental impact.
- Integration with other smart devices: Smart thermostats can be integrated with other smart home devices, such as voice assistants and security systems, creating a more interconnected and responsive home environment. For example, a smart thermostat could automatically adjust temperatures based on the presence or absence of occupants, or it could be integrated with a security system to adjust temperatures in case of an emergency.
By embracing sustainable home heating and cooling systems, homeowners can contribute to a greener future while enjoying significant savings on their energy bills. The future of sustainable home heating and cooling is bright, with ongoing advancements in technology promising even more efficient and affordable solutions. Whether you’re building a new home or upgrading your existing one, incorporating sustainable practices into your heating and cooling systems is a wise investment in your comfort, your wallet, and the planet.
General Inquiries
What are the main benefits of sustainable home heating and cooling systems?
Sustainable systems offer numerous benefits, including reduced energy consumption, lower utility bills, decreased carbon emissions, and increased property value. They also contribute to a healthier indoor environment and enhance home comfort.
How much does it cost to install a sustainable heating or cooling system?
The cost of installing a sustainable system varies depending on the type of system, home size, and local installation costs. However, government incentives and rebates can significantly offset the initial investment.
Are sustainable heating and cooling systems compatible with my existing home?
Most sustainable systems can be integrated into existing homes with varying levels of effort. A professional assessment of your home’s heating and cooling needs will help determine the best options for your specific situation.
What are some energy-saving tips for homeowners?
Simple energy-saving tips include proper insulation, sealing air leaks, using smart thermostats, optimizing window placement and shading, and utilizing energy-efficient appliances and lighting.





