
In a world increasingly focused on sustainability and resource conservation, rainwater harvesting has emerged as a practical and eco-conscious solution for homeowners seeking to reduce their reliance on municipal water supplies. Rainwater harvesting, the process of collecting and storing rainwater for various domestic uses, offers a compelling alternative to traditional water sources, providing both environmental and financial benefits.
From simple collection barrels to sophisticated filtration systems, rainwater harvesting systems come in a variety of configurations, each tailored to meet specific needs and budgets. By understanding the different types of systems, their components, and the installation process, homeowners can make informed decisions about implementing this sustainable practice in their homes.
Types of Rainwater Harvesting Systems
Rainwater harvesting is the process of collecting and storing rainwater for later use. This can be a sustainable and cost-effective way to supplement your home’s water supply, especially in areas with limited water resources or during periods of drought. Rainwater harvesting systems are becoming increasingly popular as people become more aware of the importance of water conservation.Rainwater harvesting systems can be categorized based on their complexity, storage capacity, and intended use.
Types of Rainwater Harvesting Systems
Here’s a table that summarizes the different types of rainwater harvesting systems commonly used in homes:
| Type of System | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basic System | A simple system that collects rainwater from a roof and stores it in a container. It typically includes a gutter, downspout, and a storage tank. | Easy to install and maintain. Relatively inexpensive. | Limited storage capacity. Water may not be treated for drinking. |
| Gravity-Fed System | A system that uses gravity to move rainwater from the roof to the storage tank. It typically includes a gutter, downspout, and a filter. | More efficient than a basic system. Can provide a larger storage capacity. | Requires a higher elevation for the storage tank. May not be suitable for all homes. |
| Pumped System | A system that uses a pump to move rainwater from the roof to the storage tank. It typically includes a gutter, downspout, filter, and a pump. | Can provide a large storage capacity. Can be used to distribute water to different areas of the home. | More expensive than other systems. Requires regular maintenance. |
| Integrated System | A system that is integrated with the home’s plumbing system. It typically includes a gutter, downspout, filter, pump, and a storage tank. | Can be used to provide water for a variety of uses, such as irrigation, flushing toilets, and washing clothes. | Most expensive option. Requires professional installation. |
Factors to Consider When Choosing a System
Several factors should be considered when choosing a rainwater harvesting system for your home. These factors include:* Roof size and material: The size of your roof will determine the amount of rainwater you can collect. The material of your roof will also affect the quality of the water collected. For example, roofs made of metal or asphalt shingles may release contaminants into the water.
Rainfall patterns in the area
The amount of rainfall in your area will determine the amount of water you can collect. If you live in an area with low rainfall, you may need a larger storage tank.
Water usage needs
Consider how you plan to use the rainwater. If you plan to use it for drinking, you will need to install a water treatment system.
Budget constraints
Rainwater harvesting systems can range in price from a few hundred dollars to several thousand dollars. Consider your budget when choosing a system.
Components of a Rainwater Harvesting System
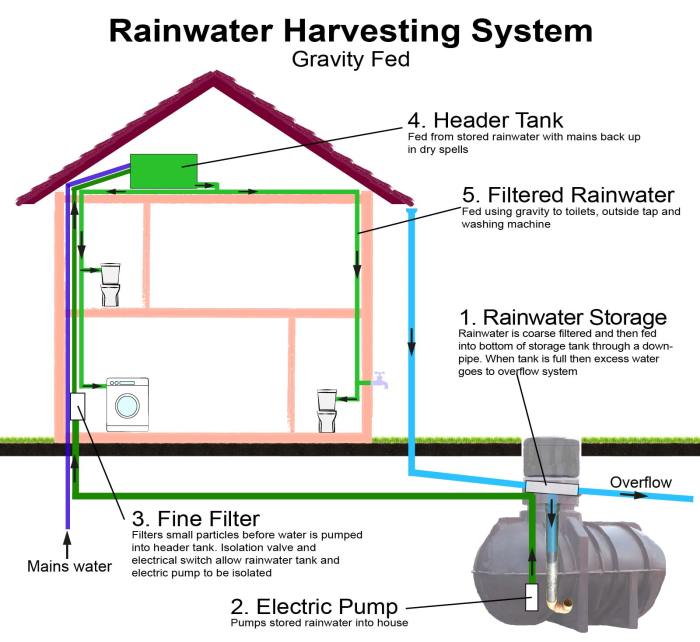
A rainwater harvesting system is comprised of several essential components that work together to collect, store, and distribute rainwater for various uses. Each component plays a crucial role in ensuring the efficient and effective operation of the system.
Roof Collection Area
The roof of a building serves as the primary collection area for rainwater. Its size and material determine the amount of water that can be harvested.
- Size: A larger roof area will collect more rainwater. The ideal roof size depends on the water needs of the household and the average rainfall in the region.
- Material: The roof material should be non-toxic and durable to prevent contamination of the harvested water. Common materials include metal, concrete, and clay tiles. Metal roofs are generally preferred for their durability and ease of cleaning.
Gutters and Downspouts
Gutters and downspouts are essential for channeling rainwater from the roof to the storage tank.
- Gutters: Gutters are installed along the edges of the roof to collect rainwater. They should be properly sized and sloped to ensure efficient water flow.
- Downspouts: Downspouts are vertical pipes that connect the gutters to the storage tank. They should be made of durable materials like PVC or galvanized steel.
First Flush Diverter
A first flush diverter is a device that diverts the initial rainwater runoff from the roof to a separate drain. This initial runoff is often contaminated with dust, debris, and pollutants, making it unsuitable for use.
- Function: The diverter typically consists of a small tank or container that collects the first flush of water. Once the tank is full, the diverter allows clean rainwater to flow into the storage tank.
- Importance: Using a first flush diverter ensures that the harvested water is clean and safe for use. It prevents contamination of the storage tank and the water supply.
Storage Tank
The storage tank is the heart of a rainwater harvesting system, where collected rainwater is stored for later use.
- Size: The size of the storage tank depends on the water needs of the household and the average rainfall in the region. A larger tank can store more water, ensuring a consistent supply even during dry periods.
- Material: Storage tanks are typically made of materials like concrete, plastic, or steel. Concrete tanks are durable but require more maintenance, while plastic tanks are lightweight and easy to install.
Filtration System
A filtration system is crucial for removing impurities from the harvested rainwater, ensuring its safety and quality.
- Types: Filtration systems can range from simple screens and filters to more advanced systems that use multiple stages of filtration.
- Importance: The type of filtration system needed depends on the intended use of the harvested water. For drinking water, a multi-stage filtration system is recommended. For irrigation, a simpler screen filter may suffice.
Pump and Distribution System
A pump and distribution system are needed to transport the stored rainwater to different points of use.
- Pump: A pump is used to pressurize the stored rainwater, allowing it to be distributed to faucets, showers, and other appliances. The pump size depends on the distance and elevation of the distribution points.
- Distribution System: The distribution system consists of pipes and fittings that connect the pump to the points of use. It should be properly sized and installed to ensure efficient water flow.
Applications of Rainwater Harvesting

Rainwater harvesting offers a versatile solution for various household needs, contributing to water conservation and reducing reliance on municipal water supplies. By collecting and storing rainwater, homeowners can utilize it for a range of purposes, minimizing their environmental footprint and potentially saving on water bills.
Watering Lawns and Gardens
Rainwater is an ideal source for irrigating lawns and gardens. It is naturally soft and free of chlorine and other chemicals commonly found in treated municipal water. Using rainwater for watering promotes healthy plant growth, as it helps to maintain soil pH levels and improves soil structure. Moreover, rainwater can be collected and stored in tanks or barrels, allowing for convenient and efficient watering throughout the year, particularly during dry periods.
Flushing Toilets
Flushing toilets accounts for a significant portion of household water consumption. Utilizing rainwater for toilet flushing can significantly reduce water usage, especially in regions with limited water resources. Installing a simple diversion system that directs rainwater to a separate toilet tank can effectively reduce reliance on potable water for this purpose. This approach minimizes water consumption without compromising sanitation.
Washing Clothes and Dishes
Rainwater can be used for washing clothes and dishes, providing a cost-effective and environmentally friendly alternative to using treated water. While it’s essential to ensure the rainwater is properly filtered to remove debris and impurities, it can be used for washing clothes and dishes without compromising hygiene. Utilizing rainwater for these tasks reduces water consumption and minimizes the environmental impact associated with treating and transporting water.
Supplying Water to Outdoor Showers and Fountains
Rainwater is an excellent source for supplying water to outdoor showers and fountains. This application minimizes the use of potable water for non-drinking purposes, contributing to water conservation. Installing a dedicated system that directs rainwater to outdoor showers and fountains ensures a consistent water supply for these features, enhancing outdoor living spaces without depleting precious water resources.
Rainwater Harvesting and Home Improvement
Rainwater harvesting can be seamlessly integrated into various home improvement projects, enhancing both the aesthetics and sustainability of your living space. By incorporating this practice, you can significantly reduce your reliance on municipal water supplies, leading to substantial cost savings and a positive impact on the environment.
Renovations and Additions
When undertaking renovations or additions to your home, rainwater harvesting can be strategically incorporated to maximize its benefits. For instance, you can install a rainwater collection system during a roof replacement or when adding an extension. Integrating the system into the existing structure ensures a cohesive and efficient design.
- Roof Design: During a roof replacement, consider incorporating a sloped roof design to facilitate efficient rainwater collection. This will enhance the effectiveness of your rainwater harvesting system.
- Gutter and Downspout Placement: Strategically position gutters and downspouts to direct rainwater towards your collection tank. This will ensure a smooth and efficient flow of water into the system.
- Tank Installation: Install a rainwater collection tank in a convenient location within your property. Choose a tank size that aligns with your water needs and the available space.
- Plumbing Integration: Connect your rainwater harvesting system to your home’s plumbing system. This will allow you to utilize rainwater for various purposes, such as flushing toilets, watering plants, and laundry.
Landscaping Designs
Rainwater harvesting can play a crucial role in creating beautiful and sustainable landscaping designs. By incorporating rainwater collection systems into your landscape, you can conserve water and promote healthy plant growth.
- Rain Gardens: Create rain gardens that capture and filter runoff water. These gardens can be designed to incorporate native plants that thrive in moist environments.
- Dry Creek Beds: Construct dry creek beds to channel rainwater away from your home’s foundation. These beds can be planted with drought-tolerant plants that add beauty to your landscape.
- Irrigation Systems: Install a drip irrigation system that utilizes rainwater to water your plants efficiently. This system can be connected to your rainwater harvesting system, minimizing water waste.
- Permeable Paving: Use permeable paving materials for driveways and walkways. These materials allow rainwater to seep into the ground, replenishing groundwater and reducing runoff.
Sustainable Building Practices
Rainwater harvesting is a cornerstone of sustainable building practices, promoting environmental responsibility and resource conservation. Incorporating this practice into your home improvement plans can contribute to a more sustainable and eco-friendly living environment.
- Water-Efficient Appliances: Choose water-efficient appliances, such as low-flow toilets and showerheads, to minimize water consumption. These appliances complement your rainwater harvesting system, creating a holistic approach to water conservation.
- Gray Water Systems: Consider installing a gray water system to reuse water from showers, sinks, and washing machines for non-potable purposes, such as watering plants. This further reduces your reliance on municipal water supplies.
- Green Roofs: Explore the possibility of incorporating a green roof into your home design. Green roofs provide insulation, reduce stormwater runoff, and enhance the aesthetic appeal of your home.
Regulations and Incentives
Navigating the legal landscape and exploring potential financial benefits are crucial steps in your rainwater harvesting journey. This section delves into local regulations, building codes, and government incentives that may influence your decision.
Local Regulations and Building Codes
Regulations concerning rainwater harvesting vary significantly across regions. It’s essential to familiarize yourself with the specific codes and ordinances applicable to your location. These regulations often address:
- Permits and Approvals: Many areas require permits for installing rainwater harvesting systems, often involving inspections to ensure compliance with safety and quality standards.
- Water Quality: Regulations might specify acceptable water quality standards for harvested rainwater, particularly for potable uses. This may involve testing and treatment requirements.
- Storage Tank Requirements: Regulations could stipulate size, material, and location restrictions for storage tanks, aiming to prevent contamination and ensure proper drainage.
- Discharge and Reuse: Regulations may define how rainwater can be discharged and reused, such as restrictions on direct discharge to sewers or limitations on using untreated water for irrigation.
Government Incentives and Rebates
Several governments and municipalities offer financial incentives to encourage rainwater harvesting. These incentives can come in various forms, including:
- Tax Credits: Some jurisdictions provide tax credits for installing rainwater harvesting systems, reducing your overall tax burden.
- Rebates: Rebates are direct financial reimbursements offered by governments or utility companies to offset the cost of installation.
- Grants: Grants provide funding to cover a portion of the project costs, often with specific eligibility criteria.
- Low-Interest Loans: Some programs offer low-interest loans to make rainwater harvesting systems more affordable.
Obtaining Permits and Approvals
The process of obtaining permits and approvals typically involves the following steps:
- Research Local Requirements: Start by contacting your local building department or water management agency to identify the specific regulations and permit requirements.
- Submit Application: Prepare and submit an application for a rainwater harvesting permit, including detailed plans and specifications for your system.
- Inspections: Your system may be subject to inspections at various stages of construction to ensure compliance with regulations.
- Obtain Approval: Once your system passes all inspections, you will receive approval to operate your rainwater harvesting system.
Conclusion
Rainwater harvesting offers a compelling solution for homeowners seeking to reduce their water footprint, save money, and contribute to a more sustainable future. By harnessing the power of nature, this practice allows you to tap into a readily available resource, lessening your reliance on municipal water supplies.
Benefits and Considerations
Rainwater harvesting presents numerous advantages, including:* Reduced Water Bills: By utilizing rainwater for non-potable purposes like watering lawns and gardens, you can significantly lower your water bills.
Water Conservation
Rainwater harvesting conserves precious water resources, reducing strain on municipal supplies and supporting sustainable water management practices.
Improved Water Quality
Rainwater is naturally soft and free from chemicals, making it ideal for watering plants and reducing the need for harsh fertilizers and pesticides.
Environmental Sustainability
By reducing your reliance on municipal water, you contribute to a greener environment and minimize the impact of water treatment processes.
Increased Property Value
A rainwater harvesting system can enhance the value of your property by showcasing your commitment to sustainability and environmental responsibility.However, it’s crucial to consider the following aspects:* Initial Investment: Installing a rainwater harvesting system requires an initial investment, but the long-term savings on water bills can offset this cost.
Space Requirements
You need adequate space to accommodate the rainwater storage tank and associated components.
Maintenance
Regular maintenance is essential to ensure the system operates efficiently and prevents potential issues.
Regulations
Local regulations may govern rainwater harvesting practices, so it’s important to familiarize yourself with them.
Water Quality
Depending on your location and roof material, you may need to filter rainwater to remove impurities before using it for certain purposes.
“Rainwater harvesting is a win-win situation for homeowners, offering both financial and environmental benefits.”
As we move towards a future where water conservation is paramount, rainwater harvesting stands as a powerful tool for homeowners to embrace sustainability and reduce their environmental footprint. By implementing rainwater harvesting systems, individuals can not only save money on water bills but also contribute to a healthier planet for generations to come. The benefits of rainwater harvesting extend beyond financial savings, encompassing a sense of self-reliance, reduced strain on municipal infrastructure, and a commitment to responsible water management.
Detailed FAQs
What are the potential downsides of rainwater harvesting?
While rainwater harvesting offers numerous benefits, potential downsides include the initial investment cost, the need for regular maintenance, and the possibility of water quality issues if the system is not properly designed and maintained. However, with careful planning and proper installation, these drawbacks can be minimized.
Is rainwater safe to drink?
While rainwater is generally safe for non-potable uses like watering plants and flushing toilets, it’s not recommended for drinking without proper treatment. Rainwater can contain contaminants like bacteria, viruses, and heavy metals, which can pose health risks. If you intend to use rainwater for drinking, consult with a water treatment specialist to ensure its safety.
How often should I clean my rainwater harvesting system?
The frequency of cleaning depends on factors like the size of your system, your local climate, and the amount of debris in your area. As a general guideline, it’s recommended to clean your gutters and downspouts at least twice a year, and to inspect and clean filters every few months. Regular maintenance ensures optimal system performance and water quality.





